View all skin. However, in some cases it is desirable to allow particles entry to the body through the skin. The reticular region lies deep in the papillary region and is usually much thicker. Cribier B. Melanin granules from melanocytes are transferred via the long processes to the cytoplasm of basal keratinocyte. The Journal of Physiology. There are many internal and external causes to skin ageing. A large area of interest in nanomedicine is the transdermal patch because of the possibility of a painless application of therapeutic agents with very few side effects. Organ covering the outside of the human body. Plast Reconstr Surg.

Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles , it can appear hairless. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Yes No. These protein fibers give the dermis its properties of strength , extensibility , and elasticity. Further information: Intrinsic and extrinsic ageing.
Related Links
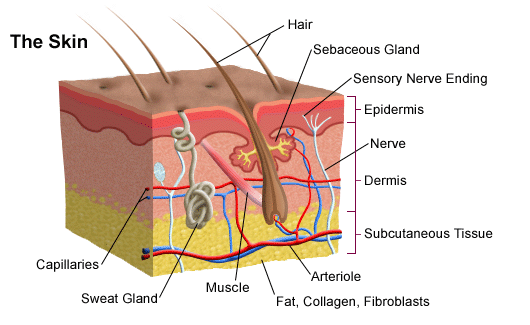
BMP signals from the epidermis inhibit the formation of placodes in nearby ectoderm. The reticular region lies deep in the papillary region and is usually much thicker. Human regional anatomy. Both the dermis and epidermis have nerve endings. The Journal of Physiology. The keratinocytes express the vitamin D receptor VDR and also contain the enzymes needed to convert vitamin D to its active form of 1, 25 dihydroxy vitamin D. The epidermis helps the skin regulate body temperature. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. While the effect of increased permeability after UVR exposure can lead to an increase in the number of particles that permeate the skin, the specific permeability of skin after UVR exposure relative to particles of different sizes and materials has not been determined. In moist places on the body Corynebacteria together with Staphylococci dominate. Hall BK. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. The skin is the largest organ of the human body. The dermis is connected to the epidermis at the level of the basement membrane and consists of two layers, of connective tissue, the papillary and reticular layers which merge together without clear demarcation.
Anatomy of the Skin
- Small circular wounds are likely to shrink, not gape".
- A large area of interest in nanomedicine is the transdermal patch because of the possibility of a painless application of therapeutic agents Skin very few side effects, Skin.
- In many experiments, Skin, gold nanoparticles 40 nm in diameter or smaller are used and have shown to penetrate to the epidermis.
- Arterial shunt vessels may bypass the network in ears, Skin, the nose and fingertips.
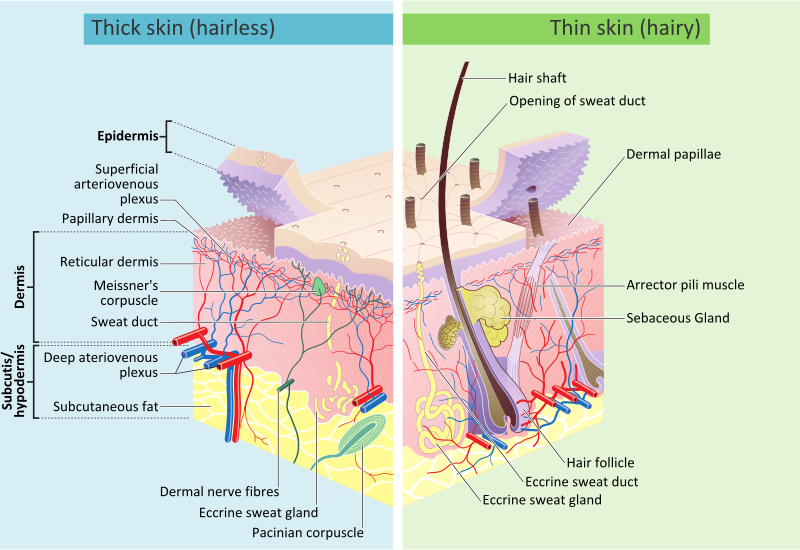
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body. For example, your head contains more hair follicles than anywhere else. But the soles of your feet have none. In addition, the soles of your feet and the palms of your hands are much thicker than skin on other areas of your body. Squamous cells. The outermost layer is continuously shed is called the stratum corneum. Basal cells. Basal cells are found just under the squamous cells, at the base of the epidermis. Melanocytes are also found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. This gives the skin its color. The dermis is held together by a protein called collagen. This layer gives skin flexibility and strength. The dermis also contains pain and touch receptors. The subcutaneous fat layer is the deepest layer of skin. It consists of a network of collagen and fat cells.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information Skin on official, secure websites, Skin. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, Skin, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system. One of the Skin functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature.

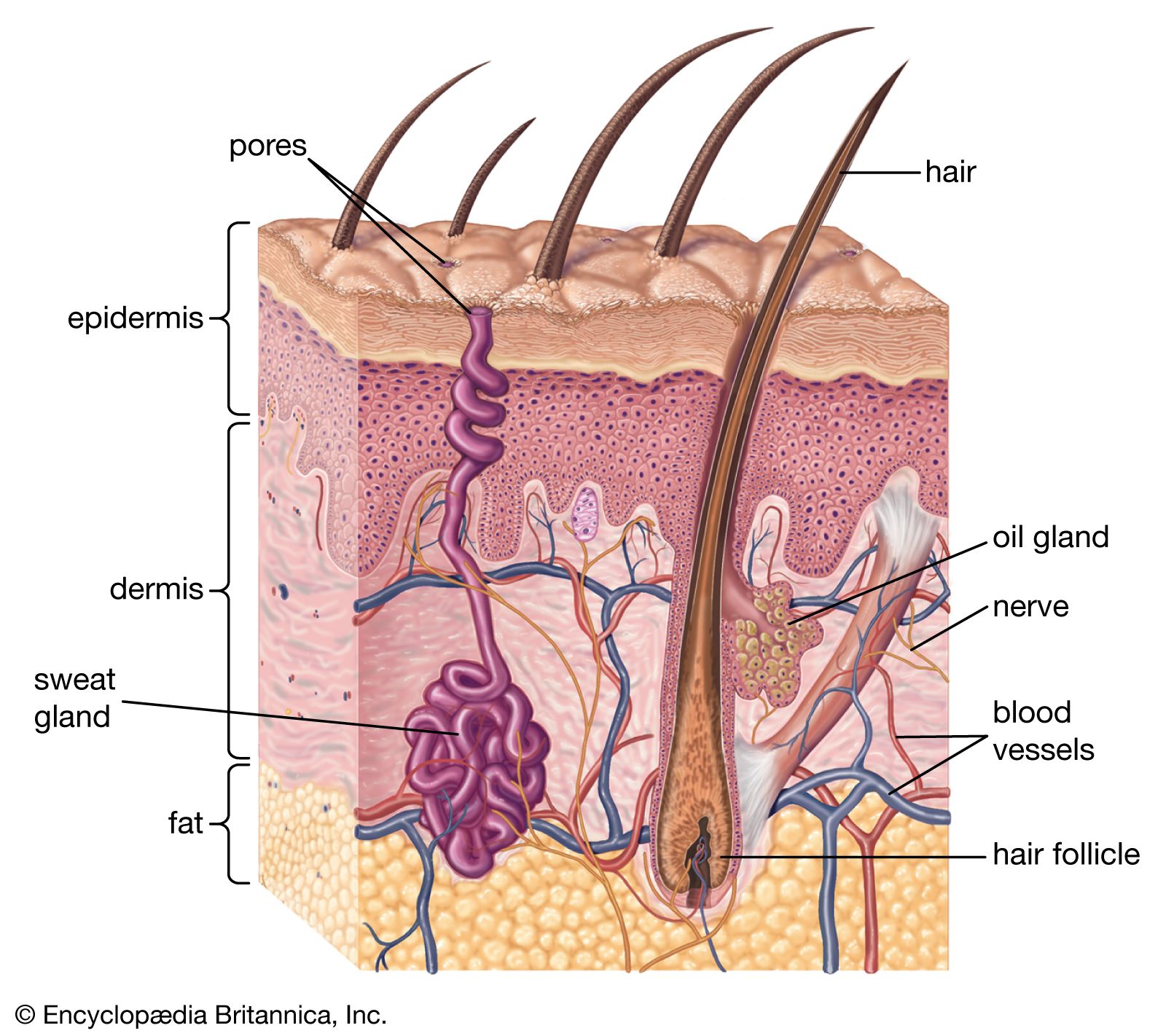
Skin. Skin layers
Skin pampers 0 auchan the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, Skin, and sensation. Other animal coveringsSkin, such as the arthropod exoskeletonhave different developmental originstructure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" from Latin cutis 'skin'. In mammalsthe skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of Skin layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the Skin musclesbonesligamentsand internal organs, Skin. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibiansreptilesand birds. All mammals have some hair on their skin, Skin, even Skin mammals like whalesdolphinsand porpoises that appear to be hairless. Skin skin interfaces with the environment and is the first Skin of defense from external factors. For example, Skin, the skin plays a key role in protecting the body against pathogens [3] and excessive water loss. Severely damaged skin may heal by forming scar tissue. This is sometimes discoloured and depigmented. The thickness of skin also varies from location to location on an organism. In humans, for example, the skin Skin under the eyes and around the eyelids is the thinnest skin on the body at 0. The skin on the palms and the soles of the feet is the thickest skin on the body at 4 mm thick. The speed and quality of wound healing in skin is promoted by estrogen. Fur is dense hair.
Facts about the skin
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is soft, to allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. Our skin is a good indicator of our general health.
ISBN Skin epidermis of fish and of most amphibians consists entirely of live cellswith only minimal quantities of keratin in the cells of the superficial layer, Skin.
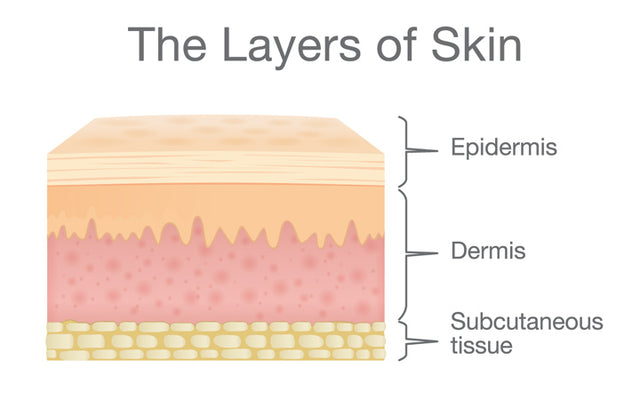
Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin, Animation
You are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.